что такое лазерная маркировка пластика
Dec 28 , 2022This section describes information ranging from the principles of plastic marking and processing to advantages grouped by laser wavelength. It introduces marking examples and the optimal laser markers for a variety of materials such as ABS, epoxy, and PET.
Plastic marking/processing types
Paint peeling
Peel the paint or printing on the target surface to bring out the contrast with the colour of the base material.

(Example) pain peeling
When the design is changed, conventional methods using printing or stamps required the printing plate to be changed. With a laser marker, you can handle it flexibly by just changing the program.
Surface peeling
Remove/engrave the surface layer with a 355 nm laser diode.

(Example) Half cut
Use a laser marker to process a cutting section. A cutter was used in the conventional method; however, there were problems such as difficult adjustment and time-consuming changeover between product types. Moreover, the method incurred costs for replacing the blade and there was a risk of the blade being left in the product.
Colour development
Irradiate a plastic target with a laser to develop a colour in the target itself.
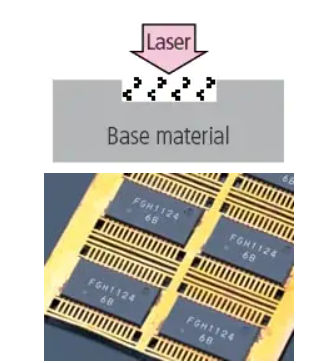
(Example) Wide-area marking on LSI
Using a laser to irradiate the plastic for colouration without engraving ensures minimal damage to the target during marking. In addition, areas of up to 330 × 330 mm can be marked all at once, mechanical equipment costs can be reduced thanks to the elimination of the need to convey the target as with conventional methods.
Welding
Use the heat of laser radiation to weld and join plastic parts.

(Example) Welding transparent and coloured plastic material
Whereas ultrasonic and vibration welding are known to adversely affect products and cause burrs due to melting, laser welding is non-contact and does not damage the product or cause burrs.
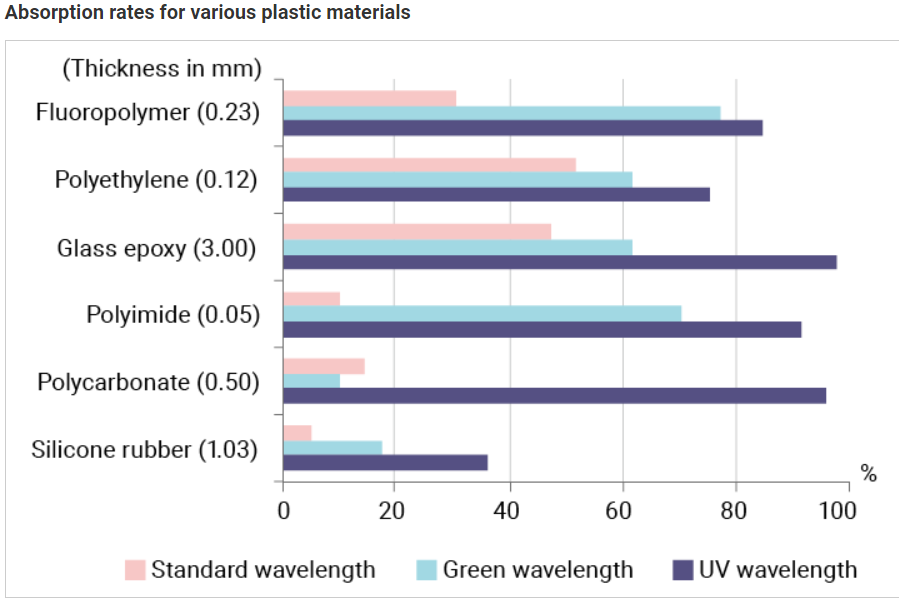
Absorption rate for plastic
Material absorption rate variations by wavelength
На приведенном ниже графике показан коэффициент передачи основного лазера (1064 нм), зеленого лазера (532 нм) и УФ-лазера (355 нм) для различных пластиковых материалов. ПВХ, АБС и полистирол, как основные, так и зеленые лазеры имеют низкий коэффициент передачи и высокий коэффициент поглощения, что обеспечивает хорошую маркировку. С другой стороны, коэффициент передачи для полиимида составляет около 30% для зеленого лазера (532 нм), но более 90% для основного лазера (1064 нм). Коэффициент поглощения сильно зависит от длины волны.